Banner artwork by ArtemisDiana / Shutterstock.com
The strategic implementation of LLMs in corporate legal operations
In today’s fast-paced corporate environment, legal departments are turning to large language models (LLMs) as innovative tools for enhancing efficiency and decision-making. With their ability to understand and generate complex language, LLMs are becoming an integral part of the legal process, from drafting documents to conducting thorough legal research.
Understanding and managing the risks effectively is crucial for legal departments to leverage LLMs safely and productively. The balance between embracing innovation and upholding the rigorous standards of legal practice is delicate. This article will explore how legal departments can navigate this spectrum, ensuring the benefits of LLMs are harnessed with minimal risk while maintaining the integrity and trustworthiness of legal work.
1. Brainstorming with LLMs: The frontier of legal innovation
Brainstorming is where the boundless potential of LLMs truly shines in the legal sector. Tasked with the creation of diverse perspectives, these models are capable of reframing challenges and devising innovative strategies that can revolutionize legal thinking and practice. LLMs facilitate idea generation on an unprecedented scale, allowing legal teams to explore a multitude of scenarios and outcomes in a fraction of the time without being limited by myopic tunnel-vision that can occur at the individual level.
The applications are manifold. Whether it’s risk management protocols that anticipate and neutralize potential legal threats, contract negotiation tactics that balance assertiveness with fairness, or crafting legal arguments that resonate with novel interpretations of the law, LLMs can inject a level of creativity and foresight that was previously unattainable.
However, with high innovation comes high risk. The risk of hallucination — where LLMs produce content that is inventive but factually unsound — is considerable. The very attributes that make LLMs powerful brainstorming partners also make them susceptible to generating content that, while persuasive, may be based on flawed reasoning or nonexistent precedents.
The very attributes that make LLMs powerful brainstorming partners also make them susceptible to generating content that, while persuasive, may be based on flawed reasoning or nonexistent precedents.
Mitigation lies in a two-pronged strategy: establishing rigorous guidelines that bind the AI's creative impulses and a thorough vetting process where every AI-generated idea is cross-examined against established legal standards and historical precedents. Additional mitigation measures can be implemented by integrating retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) into LLM workflows. RAG supplements an LLM by adding a knowledge base library to supplement and enhance the LLM outputs, creating results that are more customized for a specific subject matter or client persona. Only through a disciplined approach can legal departments harness the power of LLMs in brainstorming while ensuring that innovation does not come at the cost of accuracy and reliability.

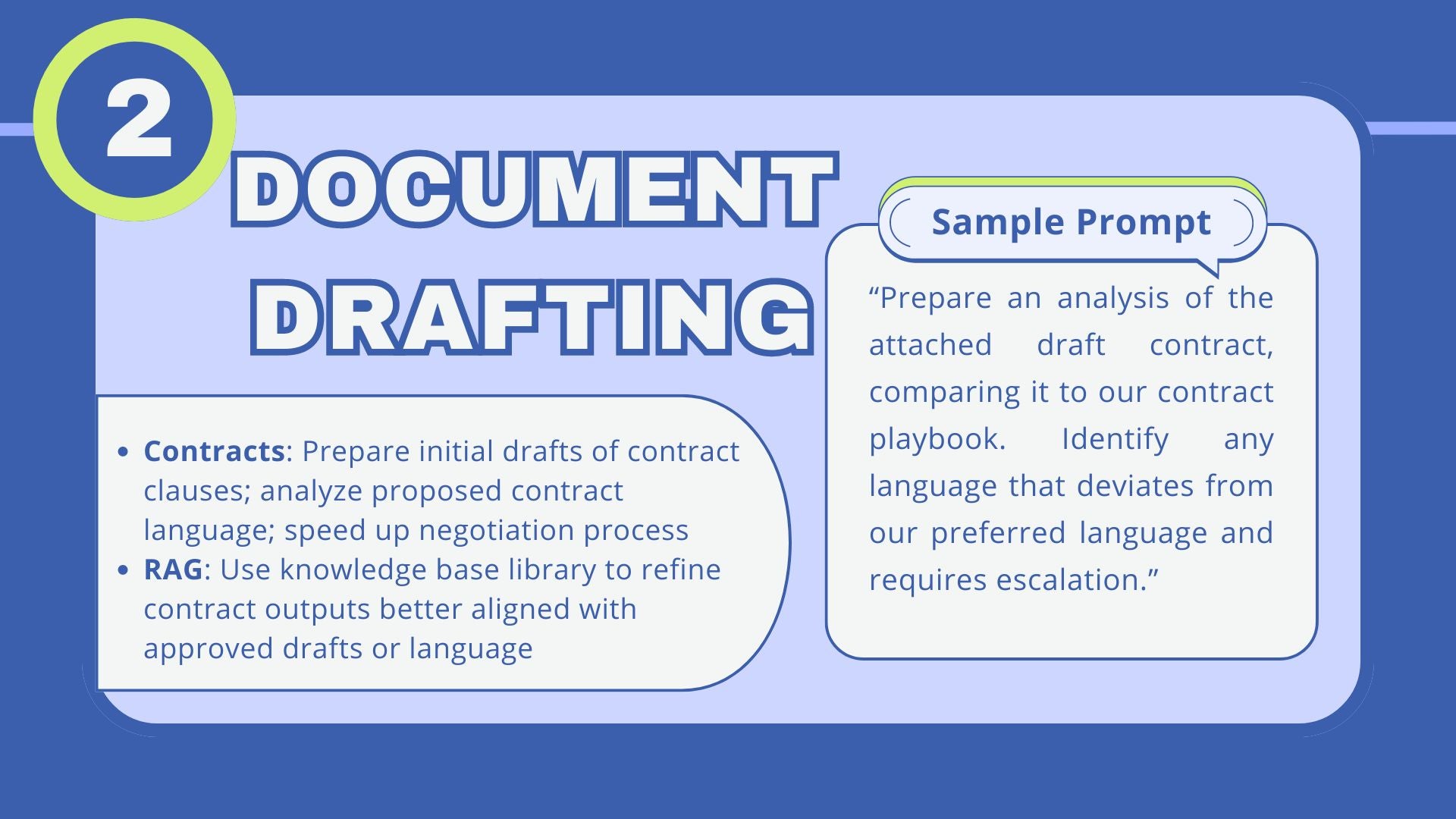
2. Authoring through LLMs: Streamlining document creation
Authoring is critical in any corporate legal department, encompassing everything from drafting nuanced contracts to preparing detailed legal memoranda. LLMs are proving to be powerful tools in this domain, offering the ability to rapidly generate legal clauses, draft comprehensive documents, and augment content creation with insightful suggestions. This capability significantly speeds up the negotiation process, aids in the drafting of memos, and facilitates the creation of coherent and well-structured legal briefs.
The application of LLMs for authoring is particularly transformative in contract law, where the generation of clauses and terms can be tailored to specific business needs while reflecting the latest legal standards. In the creation of internal memos, LLMs can assimilate vast amounts of information, ensuring that legal advice is comprehensive and considers all relevant factors. Additionally, for litigation or arbitration, the drafting of briefs by LLMs can provide a solid foundation upon which legal arguments can be built and refined.
However, the risk of hallucination presents a moderate challenge in this arena. As LLMs are tasked with creating original content, there is a potential for the production of legal clauses or terminology that may not be fully compliant with current laws or precedents, necessitating vigilant oversight. Furthermore, while an LLM can suggest a wide range of legal language, its understanding of context and nuance is not infallible.
To mitigate these risks, a system of rigorous review by experienced legal professionals is essential. Every document generated by an LLM should undergo meticulous scrutiny, with clauses and terms cross-checked against existing contracts, current laws, and legal precedents. Incorporating a multi-tiered review process, where LLM outputs are evaluated at several levels, can provide a robust filter to catch and correct any inaccuracies before the documents are finalized. For attorneys comfortable building out more advanced LLM processes, those existing contracts and collection of current laws and legal precedents could be used to build a RAG knowledge base library for that specific use case. Finally, an alternative workflow approach to consider is breaking up prompts for the various LLM outputs into discrete sets, focused on specific areas of substantive expertise. Doing so allows attorneys to exert closer control over the outputs, with errors or hallucinations likely being more apparent.
Through these strategies, LLMs can be leveraged effectively for authoring within corporate legal departments, delivering efficiency and a high degree of support, provided that their outputs are subject to thorough review and validation.
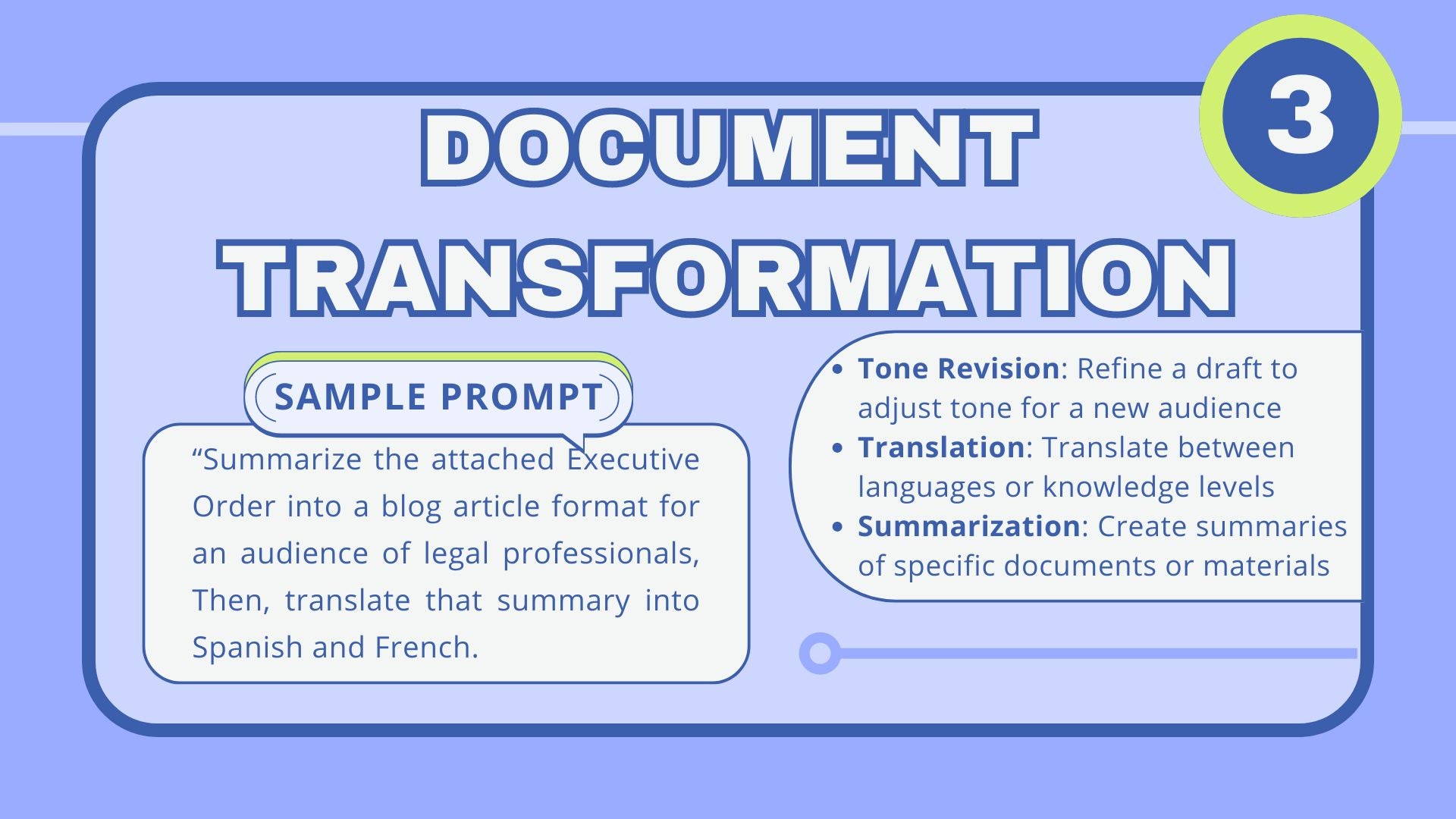
3. Transforming text and documents: The efficiency enhancer
LLMs are becoming indispensable tools for transforming texts and documents, driving efficiency and enhancing the comprehensibility of complex legal information in the digitized corridors of corporate legal departments. These AI models excel at condensing voluminous legal texts into executive summaries, translating documents for cross-border legal practices, and fine-tuning the language in legal communications to align with corporate tone and policy.
For instance, LLMs can efficiently summarize lengthy case law, enabling legal professionals to grasp the essence of judicial decisions quickly. They are equally adept at responding to requests for information (RFIs), where they can distill the core requests and legal implications. In drafting memos, LLMs ensure that the intent and nuances of legal advice are clearly communicated, saving valuable time for busy legal teams.
The transformative capabilities of LLMs, however, are not without risks. The risk of hallucination in these tasks ranges from low to moderate — summarized texts may inadvertently omit critical points, or nuances in translations might be lost, leading to potential misunderstandings. This is particularly true in the legal domain, where every detail can carry significant implications.
Mitigating these risks involves implementing a dual-review system where both legal experts and LLMs work in tandem, scrutinizing each other’s output. Moreover, positioning LLMs as auxiliary tools rather than the primary source of legal text transformation is crucial. This complementary approach allows for the utilization of LLMs’ efficiency while ensuring that the final product undergoes human oversight for accuracy and contextuality.
Corporate legal departments can significantly enhance their document processing capabilities by employing LLMs in conjunction with established review protocols. This strategic utilization not only improves productivity but also maintains the high standards of precision and reliability that are the hallmarks of the legal profession.
4. Legal research with LLMs: In-depth analysis at scale
In the world of corporate law, the expanse of precedents, statutes, and regulatory directives forms the bedrock of legal strategy and compliance. LLMs have become powerful resources in navigating this vast legal landscape, offering in-house legal departments the ability to conduct comprehensive research at an unprecedented scale. They parse through reams of legal texts to identify relevant cases, interpret statutes, and deliver analyses that inform critical legal questions.
LLMs serve as modern-day law librarians, equipped with algorithms capable of rapidly accessing and analyzing large volumes of legal information. This capacity is invaluable for tasks such as vetting precedents that support case strategies, interpreting statutes for crafting compliance frameworks, and ensuring regulatory diligence across multiple jurisdictions. In-house counsel can utilize LLMs to remain abreast of legal developments and to provide sound legal advice rooted in the most current and relevant legal information.
Despite their utility, the risk of hallucination remains but is comparatively low when the appropriate legal-focused LLMs are used. This is because LLMs in legal research primarily focus on retrieving existing factual information rather than creating new content. However, even with low risks, the implications of incorrect information in the legal field can be profound, and those risks would increase if general consumer-facing LLMs are used for legal research, as we’ve recently seen with examples like the attorney’s use of ChatGPT for legal research in Mata v. Avianca.
To ensure the reliability of LLMs in legal research, it’s crucial to adopt a verification protocol. Legal findings by LLMs should be validated with official legal databases and cross-checked with existing legal analysis. Additionally, secondary confirmations by legal experts help safeguard against the potential for oversight and ensure that the information provided by LLMs is accurate and applicable.
The strategic application of LLMs in legal research not only enriches the depth of analysis but also expands the capacity of legal departments to handle complex research tasks efficiently. With the right mitigation strategies, LLMs can be leveraged to perform a meticulous examination of legal texts, empowering legal teams with nuanced and comprehensive legal insights.

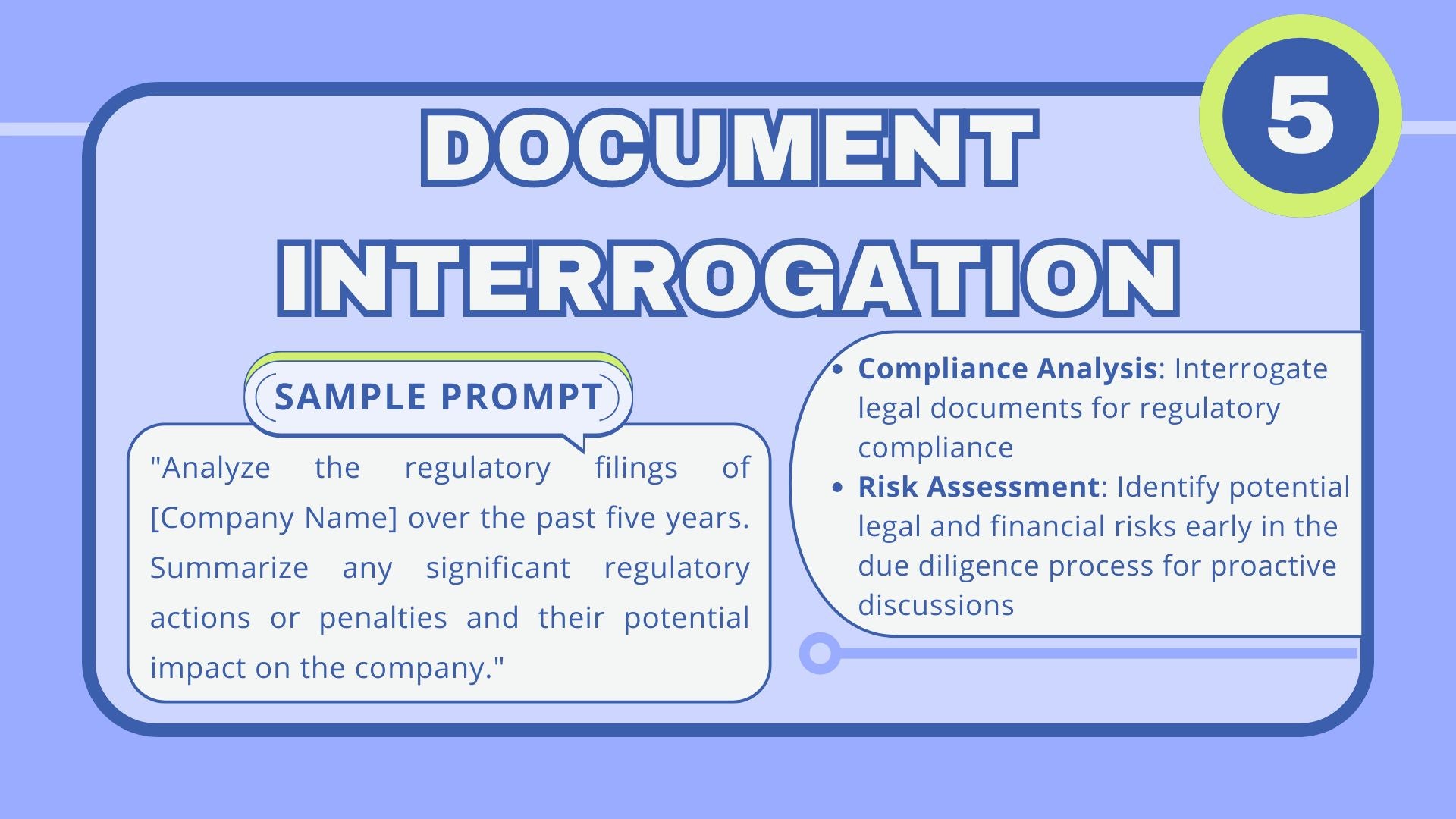
5. Interrogating documents with LLMs: Precision and diligence
Interrogation of documents represents a pinnacle of precision within the suite of LLM applications in a corporate legal setting. LLMs are deployed to meticulously sift through single or multiple documents, extracting critical data points, identifying discrepancies between contract versions, noting clause variations, and distilling specific legal points necessary for informed decision-making.
This precise interrogation extends to the due diligence process, where LLMs compare documents to ensure consistency and compliance, and during litigation, where they assist in pinpointing case-critical information across a multitude of files. Their role is fundamental when time is of the essence, and the margin for error is near zero.
Given the task’s specificity, the risk of hallucination is at its lowest. The LLM is not generating new content but instead focuses on locating and reporting specific, factual information within a predefined scope. However, vigilance is necessary even with this low risk, as the consequences of any oversight could be substantial in a legal context.
Mitigating this risk is straightforward yet essential: LLMs must be guided by controlled prompts that are precise in their aim, and their findings should be cross-referenced against authoritative documents. In-house legal teams can further buttress this approach by instituting a secondary review by human eyes to confirm the LLM’s work, ensuring no detail, however minute, is overlooked. Other workflows might include categorizing documents for analysis into varying degrees of importance and risk, dictating the level of human oversight needed for the validation of any LLM output.
Through the combination of LLMs’ meticulous nature and legal professionals’ expertise, document interrogation is transformed into a process characterized by precision and diligence. In this carefully calibrated environment, LLMs operate with a high degree of accuracy, providing legal departments with reliable tools to navigate the complex landscapes of corporate law.
Looking ahead: The importance of human counsel-AI partnership
The common thread across all these applications is the vital importance of human oversight. Legal professionals ensure the accuracy of LLM outputs and bring invaluable context and judgment to their use.
Looking ahead, the future of legal departments appears increasingly integrated with LLMs, where the efficiency of AI meets the irreplaceable expertise of human counsel. When managed with care and consideration, this partnership is set to redefine the landscape of legal services.
Disclaimer: The information in any resource in this website should not be construed as legal advice or as a legal opinion on specific facts, and should not be considered representing the views of its authors, its sponsors, and/or ACC. These resources are not intended as a definitive statement on the subject addressed. Rather, they are intended to serve as a tool providing practical guidance and references for the busy in-house practitioner and other readers.





